Once you reach your twenties, you’re expected to know a lot of things. You’ve gotten to a point where you are expected to know how to work, feed, and clothe yourself—but having an actual plan for your paychecks may not be something you’ve figured out yet. We all have a sense of the lifestyle we want to live—whether that’s buying a house, starting a business, or traveling the world—but often we don’t spend enough time on the road map that will actually get us there.
Financial planning is a subject that young people are often uncomfortable with. There are so many technical terms you’re magically supposed to understand—but what if no one ever told you which ones really matter? I get it. I went to school for design, and no one was teaching me how to make the most from my money.
Luckily, my parents understood that this is confusing for those of us just starting out and were able to answer most of my questions. So, the advice I lay out here comes to you from someone who was a novice but has learned a lot recently by making small but important changes to the way I think about my money. This stuff is scary—you’re making decisions about large amounts of money. But it would be scarier to turn 30—or worse, 40—and realize you really have no plan in place to make sure you can buy a house, help your kids through college, take a year to travel the world, or retire before you’re 80.
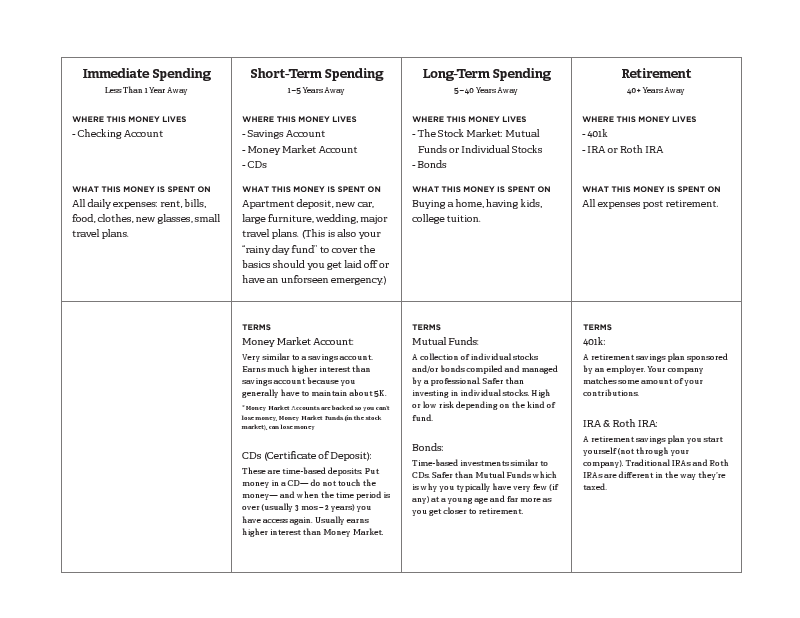
This is the first of five articles about the basics of dealing with your finances in your twenties. To start, you should be thinking about your money in categories—four categories to be exact. Four categories that are used to buy different things at different times in your life. And because they’re used at different times, for different reasons, they all live in different places. Right now we are going to go over these categories so you can keep the big picture in mind. Each of the next four articles will go in depth with one of the categories so you feel comfortable going out and making informed decisions with your money.
So let’s get into it. Oh! But before we do, if you want to make this as painless as possible, you might want to save (or maybe even print) the following chart.
All right, here we go. The first category you should think about your money in is Immediate Spending. This is the one you probably already have down pat. This is what’s in your checking account, the money that you will need within a year. This is what you use to pay your rent, bills and buy food from as well as those concert tickets you want and the new glasses you’ll need after you break your glasses at the concert. My post will focus on budgeting and my favorite way to keep track of my money painlessly.
The second category is Short-Term Spending. This is money for 1-5 years away. If you have a savings account, you already have a start on this one. But… you might not really use it for savings. It’s just… you know, that other account. While a savings account works here, I’m going to suggest thinking about a Money Market Account (which is practically the same) and/or CDs (certificate of deposit). Both simply give you higher APY (annual percentage yield, or interest rate), meaning you make more money by simply putting your money in the right place. This money is spent if you need to put a deposit down on an apartment or a new car, want to travel for a few months or in case you get unexpectedly laid off from work.
The third category is Long-Term Spending. This is the money you use to buy a house and start a family, start your own business, or to go back to school. You want to feel confident that you will not need to touch this money until 5 to 40 years from now. You want to invest this money in the stock market and/or in bonds. For all our sanity, when we talk about the stock market, we’re going to keep it to investing in mutual funds and individual stocks. Yes, the stock market can definitely seem scary, but I promise to make it as simple as I can.
The last category is Retirement. Please don’t neglect this one, guys. It’s such an easy one, and starting early has an enormous impact on how much money you retire with. This is the money for all expenses you will have post-retirement. It goes into a 401k, an IRA (individual retirement account), a Roth IRA—or some combination of these.
Okay, those are the basics. Four categories of money for four different types of spending. We will go in-depth with each category in each of the next four articles. Hopefully, by the end of this series, you’ll have a better understanding of how to start plotting your financial road map. I promise, no matter how little you have to save it isn’t as hard as it seems. Once you plot your road map, you’ll be well on your way.

Photo by Meaghan Morrison